Chapter-13 PMA Write-up
Chapter 13 challenges the walkthrough
This chapter discussed data encoding and encryption techniques.
I will try to perform full analysis and then answer the labs questions.
1- Lab13-01.exe:
Basic Analysis:
First, the tsample hash:
sha256: 71a295247ba7419f9f9dea8098e6867182bb80f53c98eb0f59192a6557a51249
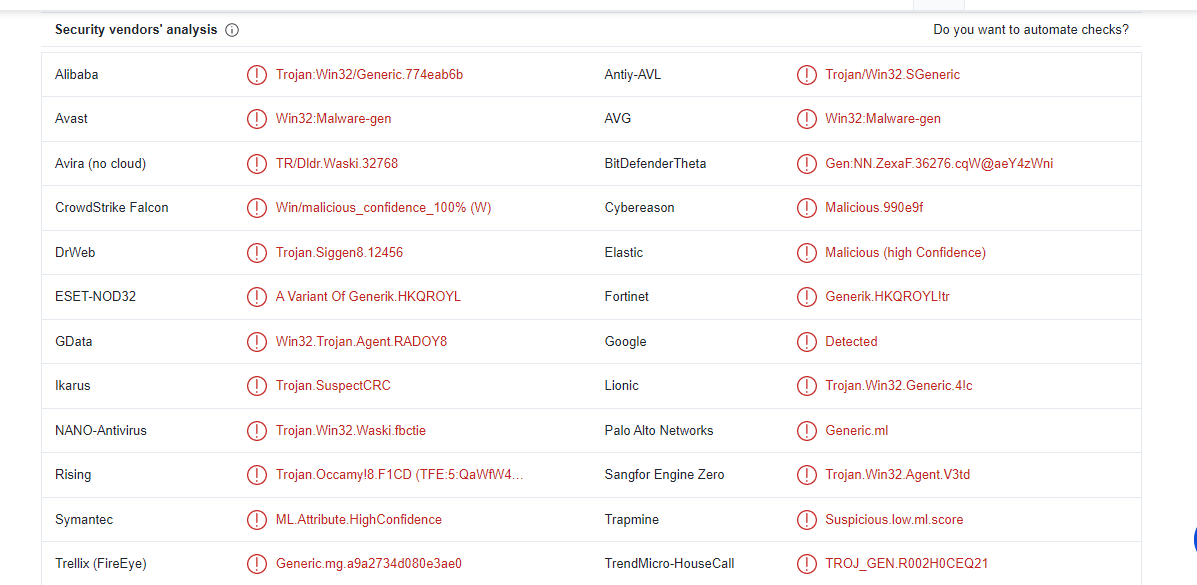
And search with this hash in Virus total
So, our sample is detected as a trojan.
Then, we will extract strings from the sample and we will find some interesting ones
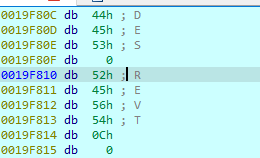
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/
InternetReadFile
InternetCloseHandle
InternetOpenUrlA
InternetOpenA
WININET.dll
GetCommandLineA
Mozilla/4.0
http://%s/%s/
The first string is a Base64 string and then we have some import to connect with URL and read data from a handle opened by the InternetOpenUrl, then we have a user agent and URL format.
Now, let’s perform dynamic analysis.
When we run this sample and monitor network connections via wireshark we will find that this sample will query www.practicalmalwareanalysis.com which doesn’t appear in strings as we saw.
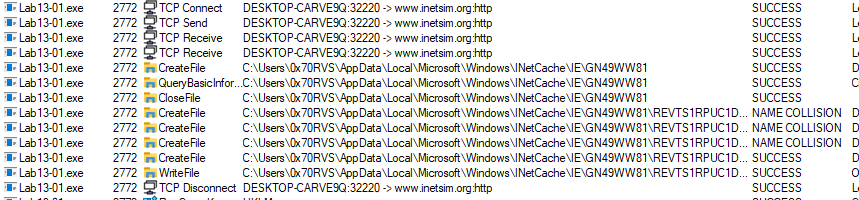
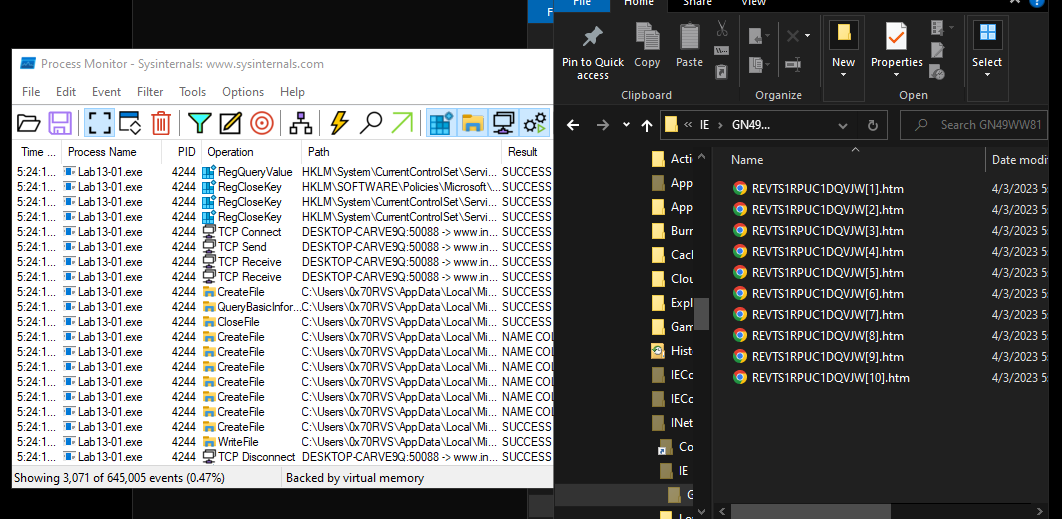
And if we see malware activities in procmon we will see that the malware will create files in C:\Users\UserName\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCache\IE\GN49WW81
If we look at wireshark again we will find that the malware will download files from URL using HTTP GET requests and if we open packets we will find that the full URL is look like the URL format we found in strings
Advanced Analysis:
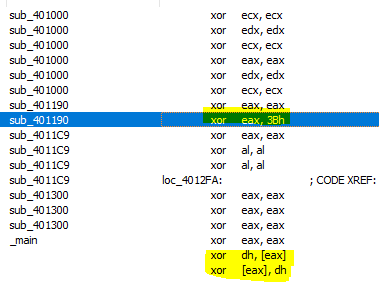
We will start advanced analysis by hint from question2 by searching in IDA for all occurrences of xor. We will find too many xoring register with itself but also we will find three interesting
The first one seems to be single-byte xor encoding, it placed in sub_401190 and if we view xref for this function we will find only one calling from sub_401300, by look at this function we will find some suspicious activities.
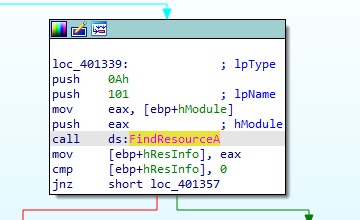
First, it will call GetModuleHandleA then FindResourceA which searchs for a resource called 101
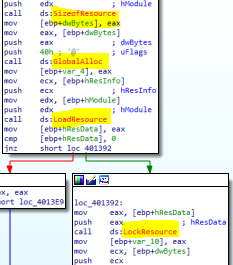
After that it will get resource size, allocate bytes from the heap, load the resource and then it will retrive a pointer to this resource in memory
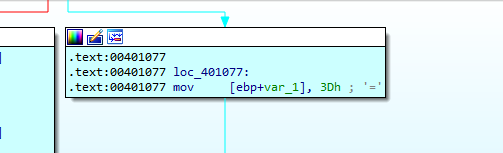
After that it will the function that contain our xor operation.
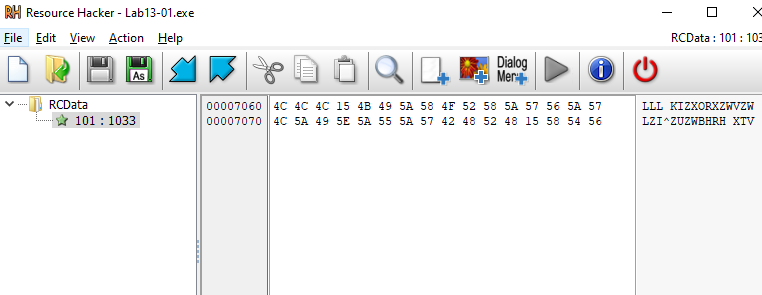
I opened Resource Hacker to extract this resource from sample and i found stearm of hex bytes
I wrote simple decoder with the key found in assembly
hex_values = input(" ")
encodedstr = bytes.fromhex(hex_values)
decodedstr = " "
key = 0x3B
for byte in encodedstr:
decodedstr += chr(byte^key)
print (decodedstr)
And i got the domain we found in dynamic analysis

After decoding domain name the malware wil initiates use of the Winsock DLL by a process using WSAStartup.
Then it will sleep and call sub_4011C9 and then sleep again, we will ignore sleep functions now and dive into sub_4011C9.
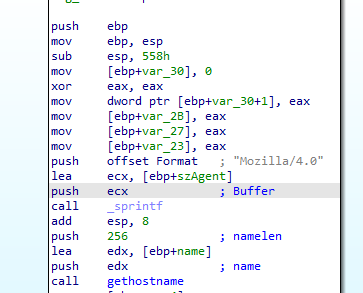
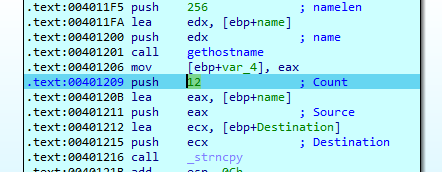
First, this function will push the user agent we found in strings Mozilla/4.0 and then get the host name
Then the malware will call strncpy which copies the first num characters of source to destination, in our case it will copy the first 12 bytes from the hostname
Then the cut name will passed to sub_4010B1, This function was very complicated, so i start to degbug it.
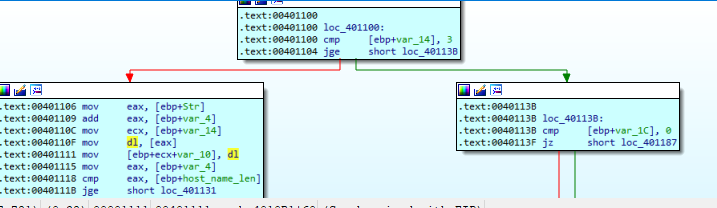
First, it will take the passed string length (which is 12) and it will take two different branches based on var_14.
for the left branch (Appoligize me if I was wrong I mean that one on 00401106) will first take three chars from passed string (DES) and then goto the other branch and passing these chars to sub_401000, inside these function we will find that this is a Base64 encoding routine, we can ensure that from the Base64 reference string that we found in strings
and Base64 padding char
After execute this function to the end we can see 4 bytes encoded
After execute full routine we will see the fully encoded string
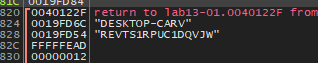
as we see that the file name requested by malware in dynamic analysis
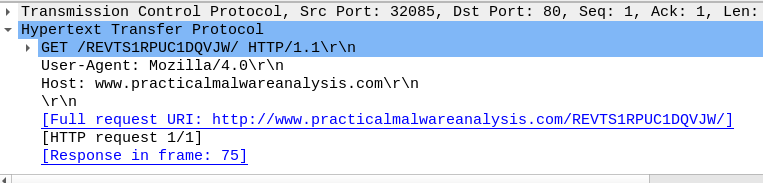
After that the malware will call InternetOpenA with UserAgent and then will call InternetOpenUrlA with full resolved URL http://www.practicalmalwareanalysis.com/REVTS1RPUC1DQVJW/
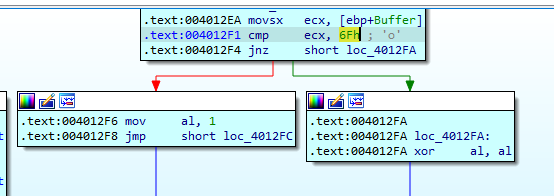
If the connection succeed it will read data from This url using InternetReadFile and it will check if this data is equal to 6Fh it will return 1 and if not it will return 0
In main it will sleep and then check from return value from sub_4011C9 if it was 0 malware will repeat connection and if it was 1 it will terminate use of the Winsock2 DLL using WSACleanup and exit
Questions:
Q1: Compare the strings in the malware (from the output of the strings command) with the information available via dynamic analysis. Based on this comparison, which elements might be encoded?
The elements will encoded by malware are:
- The domain name => Using single-byte xor
- The file name which will downloded from this domain (Host name) => Using Base64
Q2: Use IDA Pro to look for potential encoding by searching for the string xor. What type of encoding do you find?
Single-byte xor encoding
Q3: What is the key used for encoding and what content does it encode?
The key is 0x3B
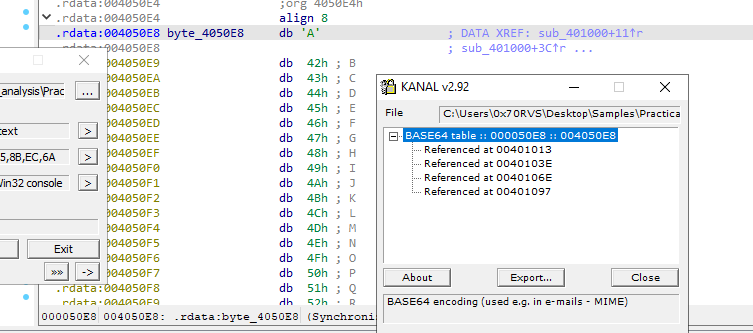
Q4: Use the static tools FindCrypt2, Krypto ANALyzer (KANAL), and the IDA Entropy Plugin to identify any other encoding mechanisms. What do you find?
For some reasons i couldn’t install IDA plugins but KANAL found refernce to Base64 table in 004050E8 which contain Base64 refernce string
Q5: What type of encoding is used for a portion of the network traffic sent by the malware?
Base64
Q6: Where is the Base64 function in the disassembly?
in sub_4010B1
Q7: What is the maximum length of the Base64-encoded data that is sent? What is encoded?
Base64 convert every 3 bytes to 4 bytes and the maximum length in our case is 12 bytes so the maximum length of encoded data will be 16 bytes, and the host name will be encoded
Q8: In this malware, would you ever see the padding characters (= or ==) in the Base64-encoded data?
If the host name length is less than 12 bytes and it’s not multiple of 3.
Q9: What does this malware do?
This malware will probe its C2 server every 31 second and if it receive a certain command 6F it will exit.
Lab finished
2- Lab13-02.exe:
Basic Analysis:
With basic static analysis i didn’t find anything interesting so i started to perform basic dynamic analysis
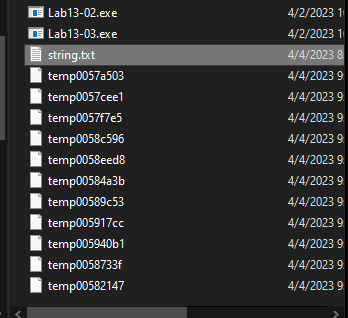
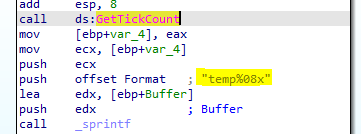
After running this malware it will create files in its directory with naming format temp%08x
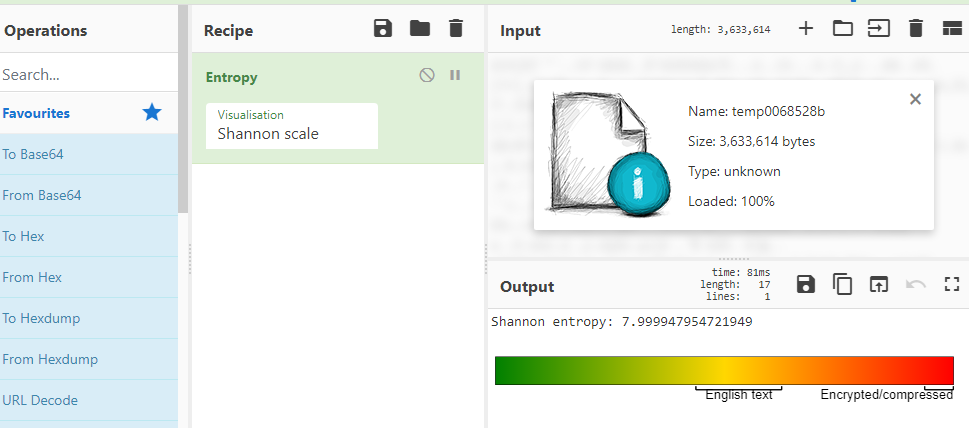
If we want to open this file we will get a random data, and if we check its entropy with cyber chef, we will find that file’s entropy is very high
So, this files is encrypted or encoded.
Advanced Analysis:
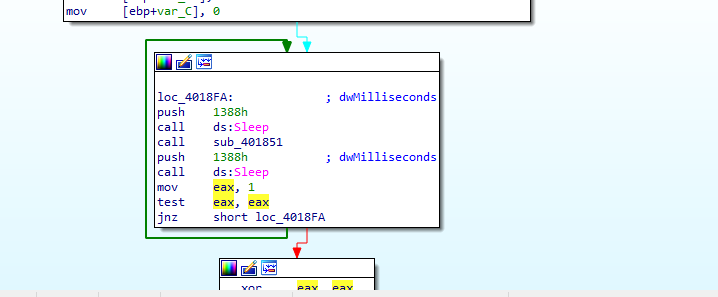
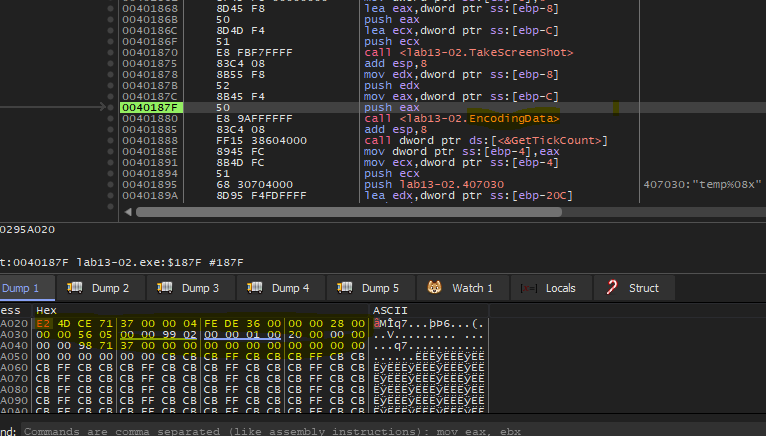
When we load this malware into IDA and view main method, we will see that this malware will sleep and then call sub_401851 and then sleep again and this process is repeated endlessly because
So, let’s dive into sub_401851.
Inside this function, there are three calls to functions and string format identical to the name of created files.
Let’s take dive into these functions one by one.
Inside sub_401070 we will see calling to many import like
- GetSystemMetrics: Retrieves the specified system metric and with parameters passed to it (0,1) it will get width and height of the screen of the primary display monitor
- GetDesktopWindow: Retrieves a handle to the desktop window
- GetDC: retrieves a handle to a device context (DC) for the client area of a specified window or for the entire screen
- CreateCompatibleDC: creates a memory device context (DC) compatible with the specified device.
- CreateCompatibleBitmap: creates a bitmap compatible with the device that is associated with the specified device context.
- SelectObject: selects an object into the specified device context (DC)
- BitBlt: performs a bit-block transfer of the color data corresponding to a rectangle of pixels from the specified source device context into a destination device context
- GetObject: retrieves information for the specified graphics object
- GlobalAlloc: Allocates the specified number of bytes from the heap
This combination of APIs indicate that this malware will take a screen shot for the Desktop and place it in the heap.
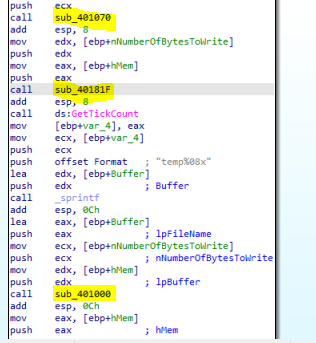
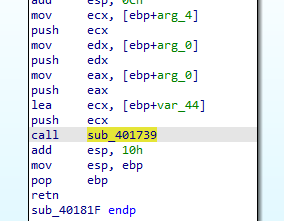
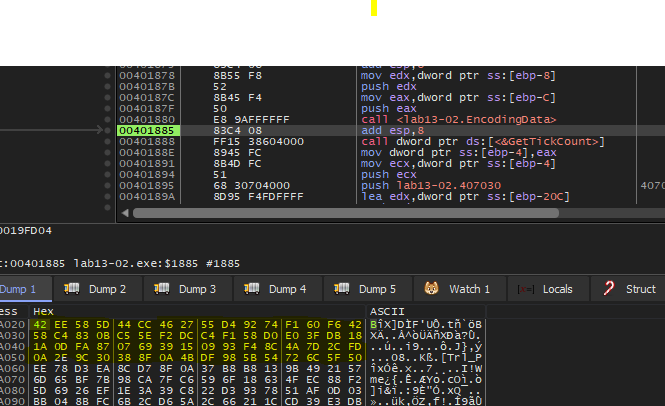
After the function is return, sub_40181F will be called with two parameters
- hMem: Looks like a handle to the memory address that contain the screen shot
- nNumberOfBytesToWrite
Inside this function we will find a call to another function sub_401739 that will take hMem and nNumberOfBytesToWrite
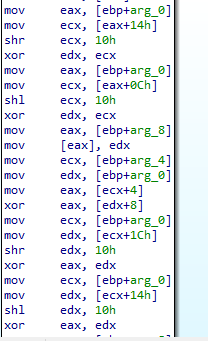
Inside sub_401739 we will see many logic operations and xor seems to custom encoding algorithm
So, this function encode the content that will be in the files created by this malware.
Return to the main logic function, the malware will call GetTickCount which retrieves the number of milliseconds that have elapsed since the system was started and then push the return value with file name format to sprintf to construct the file name
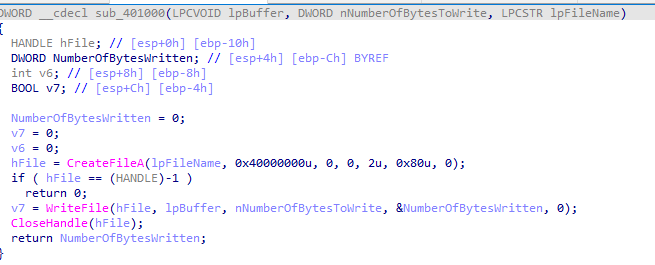
Then, the malware will call sub_401000.
This function will take
- The file name contructed above
- hMem which point to encoded data
- NumberOfBytesToWrite
Inside this function we will see CreateFileA and WriteFile. So, this function that will create files and write the encoded data into it.
For now, we’ve got a good idea of what this malware does, but we can get more details with debugging this malware so let’s do it.
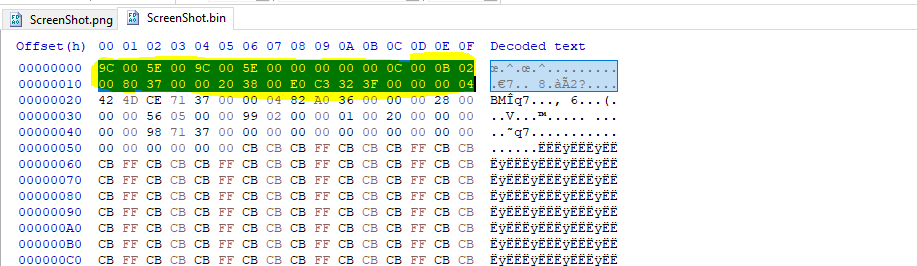
Let’s begin with sub_401070, after debuging it I follow hMem in memory map inside x64dbg and then dump this memory space to file and remove some bytes with hex editor to remove extra bytes
and then saving the file with png extension, and as i expected the malware took a screenshot.
The function that encode the data was very complex so i doesn’t debug it and the last function was very clear it just create file and then write the encoded data to this file. So, let’ move to Lab question.
Questions:
Q1- Using dynamic analysis, determine what this malware creates.
This malware will create a file every 5 seconds.
Q2- Use static techniques such as an xor search, FindCrypt2, KANAL, and the IDA Entropy Plugin to look for potential encoding. What do you find?
If we search on IDA for xor we will find that almost occurrence will be in encoding function, and plugins doesn’t show any thing maybe because the used algorithm is a custom algorithm
Q3- Based on your answer to question 1, which imported function would be a good prospect for finding the encoding functions?
I think if we reverse our analysis direction CreateFileA and WriteFile can help us to find encoding routine.
Q4- Where is the encoding function in the disassembly?
In sub_40181F specially sub_401739.
Q5- Trace from the encoding function to the source of the encoded content. What is the content?
Screenshot of monitor.
Q6- Can you find the algorithm used for encoding? If not, how can you decode the content?
Yah, I found it and this algorithm is xor operations so it’s reversible so to decode the encoded content we will perform the same algorithm to decode.
Q7- Using instrumentation, can you recover the original source of one of the encoded files?
Yup, I can recover the orginal data because the algorithm is reversible. So, we can dump encoded bytes after encoding function, clean it in hex editor and then restart the debugger a replace these bytes with original bytes, then execute the encoding funtion and get decoded bytes.
1- Encoded Bytes:
2- pass it to encoding function in the debugger:
3- get the decoded (original) bytes:
Lab finished
3- Lab13-03.exe:
Basic Analysis:
The sample hash:
SHA256: 86054002565c929215b82615477652d24379b9119bc33ef7f41706ee7e125379
If we search for this hash in virus total, we will see that this malware is aa trojan and try to connect to certain domain name and try to execute commands on the system
By looking at strings output we will get some interesting strings:
1- Custom Base64 indexing string
CDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzab0123456789+/
2- Domain name
www.practicalmalwareanalysis.com
3- command process
cmd.exe
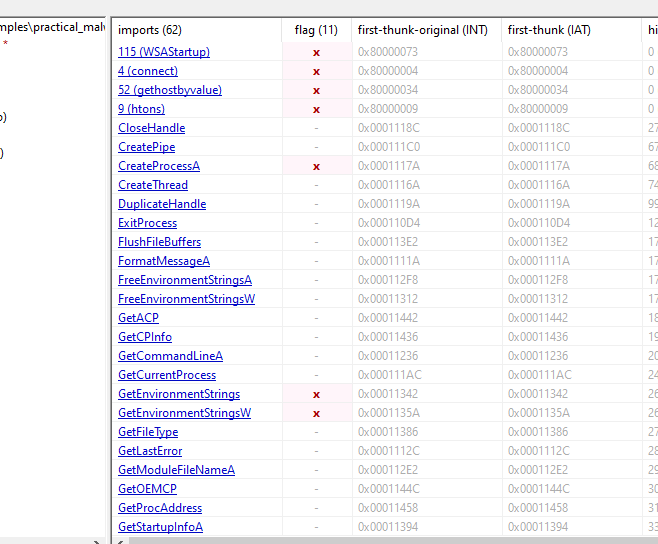
If we open PEstudio to see import we will get some interesting ones
So, this malware will tyr to connect to extracted domain name and may be create process or threads.
Let’s run this malware to get more information.
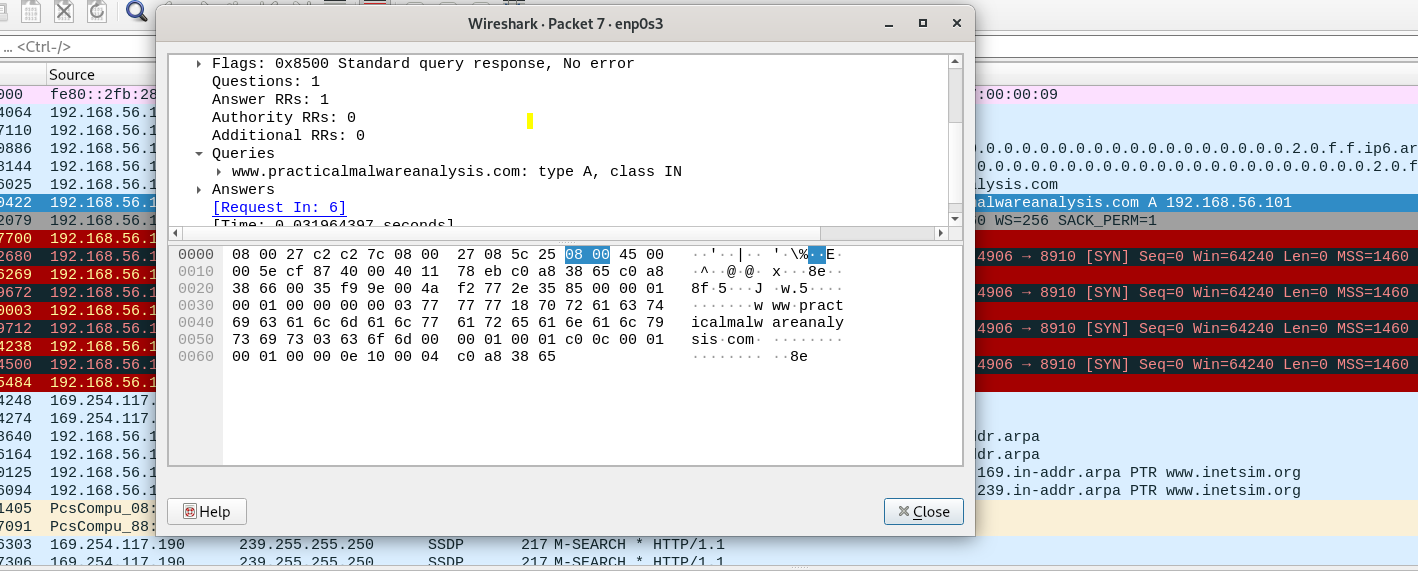
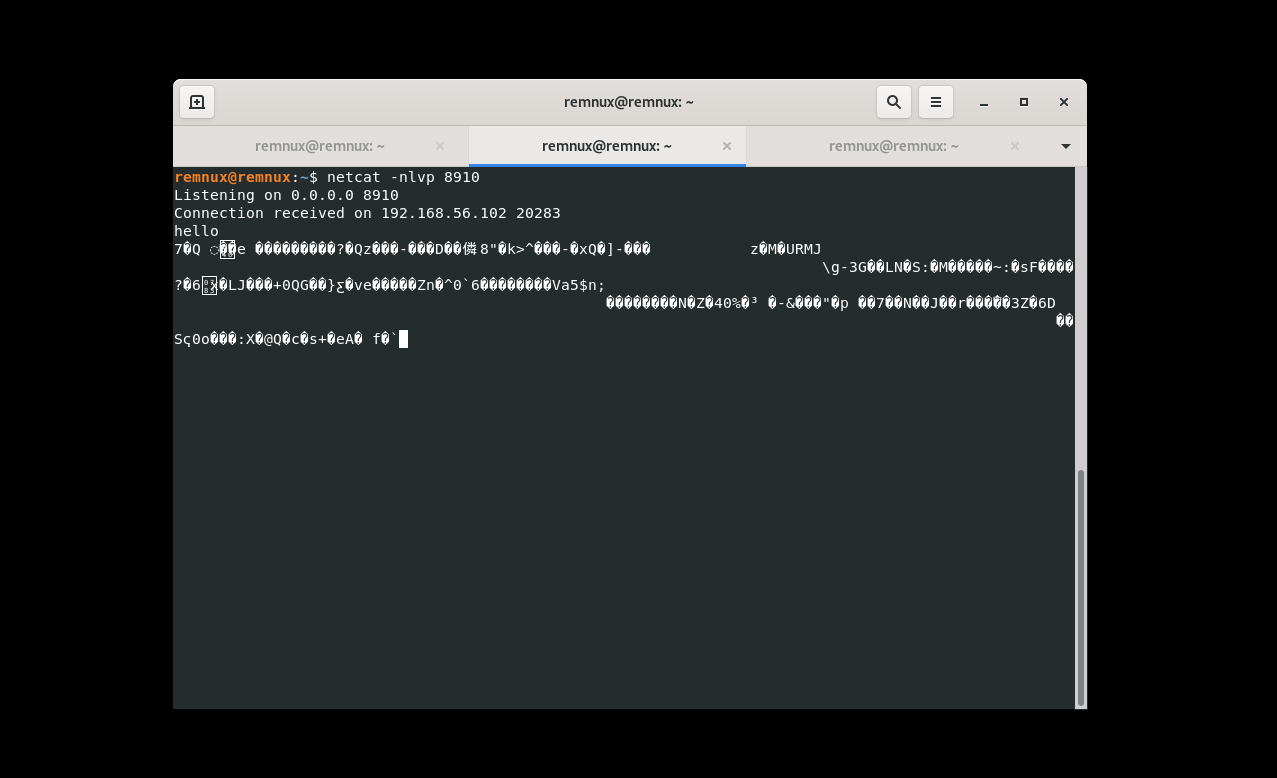
If we open wireshark to see traffic while running the malware we will see that it will query for the extracted domain name and then there are failed connection on port no 8910 after that
I can’t make successful connections with wireshark, so I open netcat and set it as a listener on port 8910 and i get some encrypted data
And if we llok at process explorer we will find that the malware has a cmd.exe as a child process, so this encrypted data received from C2 server maybe a command to execute on the system
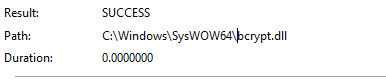
If we take a look for procmon we will find that the malware opens bcrypt.dll which is windows cryptographic Primitives Library provides a set of functions that perform basic cryptographic operations such as creating hashes or encrypting and decrypting data
Advanced Analysis:
So, loading our sample to IDA and open main function we will see that there are calls to (sub_401AC2 , WSAStartup , WSASocketA , gethostbyname , htons , connect , sub_4015B7)
We are interested of sub_401AC2 and sub_4015B7. So, let’s take them one by one.
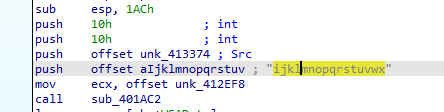
sub_401AC2 takes four arguments (offset aIjklmnopqrstuv , offset unk_413374 , 16, 16 )
The first argument seems to be a key for something but we will see, let’s dive inside it.
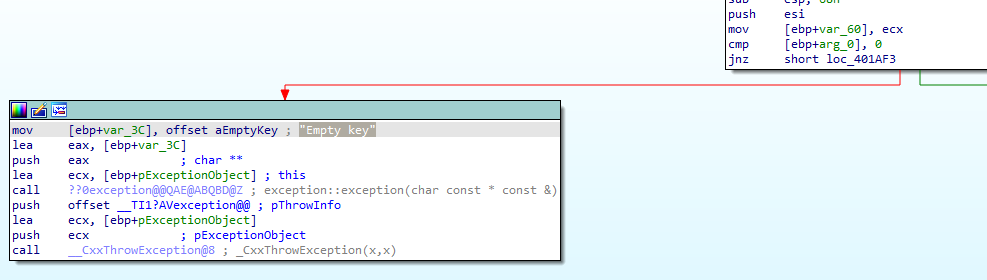
First thing, the function will check the first argument if it equal to zero it will make an exception to Empty key
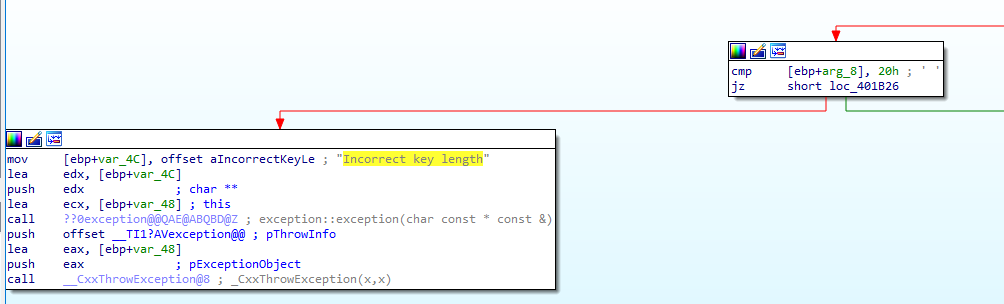
If not the malware will check third argument size with (10h, 18h, 20h) if not equal to one of these values it will make an exception to Incorrect key length
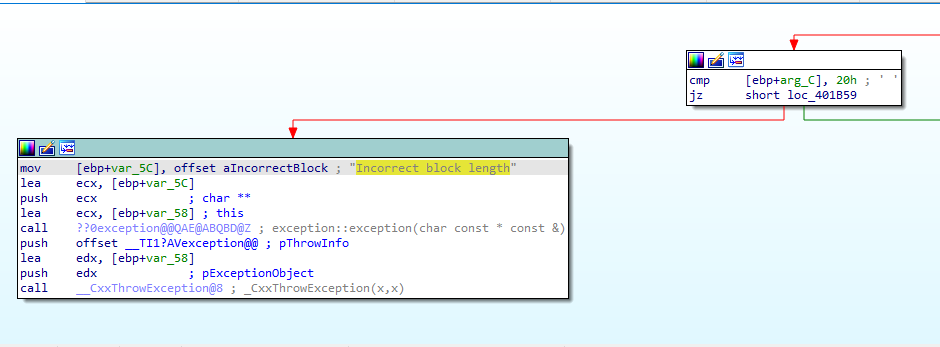
and then will repeat this comparision to forth argument with same values and also if not equal to one of these values it will make an exception to Incorrect block length
If we go deep in this function we will find a huge number of logic operations includes xor will performed
So, now we have an encryption function but we don’t what if this is a known algoritm or not.
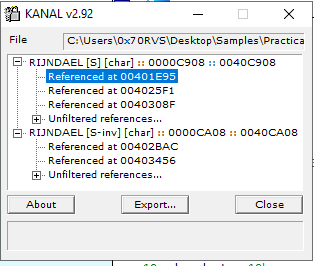
I opened KANAL to search for any encryption algorithms and this what I get
KANAL identify AES algorithm used in our sample, the first address AES used at 00401E95 which is in our function. So, this function perform AES encryption and this algorithm is symmetric encryption and the key we can get it from the funtion’s arguments (ijklmnopqrstuvwx)
After this function execute, then the malware will prepare to connect with C2 server and then call sub_4015B7.
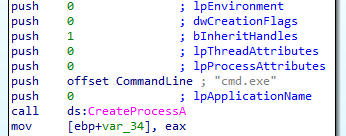
Inside this function, the malware will create two pipes and will create process with cmd.exe name
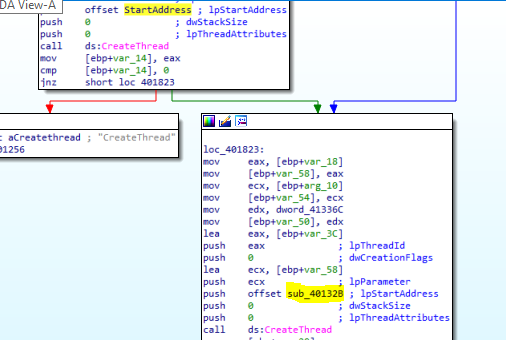
After that the malware will create two threads inside cmd process one will run function under the name of StartAddress and other unnder the name of sub_40132B
Here I really get lost in details inside these function. So, I decide to get a step back and I notice that I didn’t see the custom Base64 index string. So, I opened strings window to search for it and i found it in sub_40103F and get xrefs for this function and I found that the origin of this function is StartAddress which will be run in the frist created thread
sub_40103F => sub_401082 => StartAddress
So, for now, we can say that this malware will receive a custom Base64 encoded commands to execute on the machine then it will encrypt the response with the AES algorithm back to the C2.
Questions:
Q1- Compare the output of strings with the information available via dynamic analysis. Based on this comparison, which elements might be encoded?
Response to commands passed from C2 server
Q2- Use static analysis to look for potential encoding by searching for the string xor. What type of encoding do you find?
The type of encoding in this malware is custom Base64 encoding.
Q3- Use static tools like FindCrypt2, KANAL, and the IDA Entropy Plugin to identify any other encoding mechanisms. How do these findings compare with the XOR findings?
By using KANAL, we will find that the malware will also use AES ecryption.
Q4- Which two encoding techniques are used in this malware?
- Custom Base64 encoding
- AES encryption
Q5- For each encoding technique, what is the key?
- Custom Base64 :
CDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzab0123456789+
- AES:
ijklmnopqrstuvwx
Q6- For the cryptographic encryption algorithm, is the key sufficient? What else must be known?
After searching for more information about AES algorithm I found that the key only is not sufficient but you need to know also some information like cipher mode
Q7- What does this malware do?
As I said before questions, this malware wil connect to C2 server and then receives command to execute. So, this malware is a reverse shell.